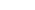[2017] Identification, characterization, immobilization, and mutational analysis of a novel acetylesterase with industrial potential (LaAcE) from Lactobacillus acidophilus
journal : BBA General Subjects, 2017, 28962
content
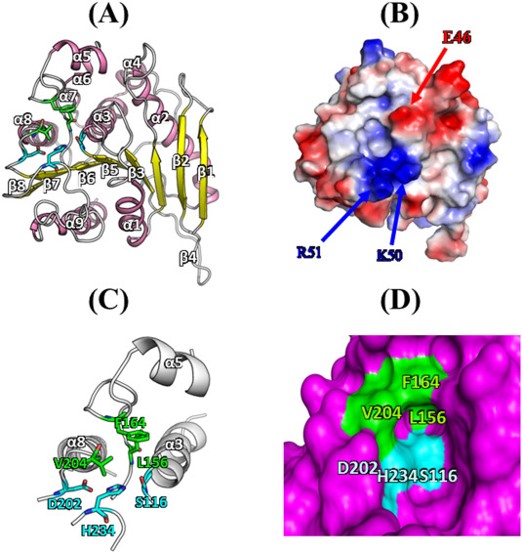
ABSTRACT: Lactic acid bacteria, which are involved in the fermentation of vegetables, meats, and dairy products, are widely used for the productions of small organic molecules and bioactive peptides. Here, a novel acetylesterase (LaAcE) from Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM was identified, functionally characterized, immobilized, and subjected to site-directed mutation for biotechnological applications. The enzymatic properties of LaAcE were investigated using biochemical and biophysical methods including native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, acetic acid release, biochemical assays, enzyme kinetics, and spectroscopic methods. Interestingly, LaAcE exhibited the ability to act on a broad range of substrates including glucose pentaacetate, glyceryl tributyrate, fish oil, and fermentation-related compounds. Furthermore, immobilization of LaAcE showed good recycling ability and high thermal stability compared with free LaAcE. A structural model of LaAcE was used to guide mutational analysis of hydrophobic substrate-binding region, which was composed of Leu156, Phe164, and Val204. Five mutants (L156A, F164A, V204A, L156A/F164A, and L156A/V204A) were generated and investigated to elucidate the roles of these hydrophobic residues in substrate specificity. This work provided valuable insights into the properties of LaAcE, and demonstrated that LaAcE could be used as a model enzyme of acetylesterase in lactic acid bacteria, making LaAcE a great candidate for industrial applications.
KEYWORDS: LaAcE, acetylesterase, Lactobacillus acidophilus

Author : Ying Wang, Bum Han Ryu, Wanki Yoo, Chang Woo Lee, Kyeong, Kyu Kim, Jun Hyuck Lee, T. Doohun Kim*
Journal : BBA General Subjects, 2017, 28962
Publication Date : 2017.10.10

This publication is from Prof. Doohun Kim’s lab