[2017] Artificially-built solid electrolyte interphase via surface-bonded vinylene carbonate derivative on graphite by molecular layer deposition
journal : Journal of Power Sources 2017 (370) 131-137
content
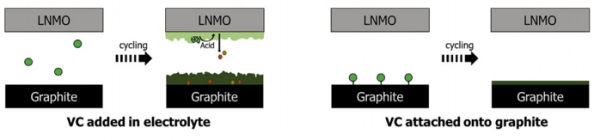
ABSTRACT: Vinylene carbonate (VC) is attached in a ring-opened form on a graphite surface by molecular layer deposition (MLD) method, and its role as a solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) former is studied. When VC is added into the electrolyte solution of a graphite/LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 (LNMO) full-cell, it is reductively decomposed to form an effective SEI on the graphite electrode. However, VC in the electrolyte solution
has serious adverse effects due to its poor stability against electrochemical oxidation on the LNMO positive electrode. A excessive acid generation as a result of VC oxidation is observed, causing metal dissolution from the LNMO electrode. The dissolved metal ions are plated on the graphite electrode to destroy the SEI layer, eventually causing serious capacity fading and poor Coulombic efficiency. The VC derivative on the graphite surface also forms an effective SEI layer on the graphite negative electrode via reductive decomposition. The detrimental effects on the LNMO positive electrode, however, can be avoided because the bonded VC derivative on the graphite surface cannot move to the LNMO electrode.
Consequently, the graphite/LNMO full-cell fabricated with the VC-attached graphite outperforms the cells without VC or with VC in the electrolyte, in terms of Coulombic efficiency and capacity retention.
KEYWORDS: Lithium-ion batteries, Graphite, Surface modification, Molecular layer deposition, Vinylene carbonate, LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4

Author : Seulki Chae, Jeong Beom Lee, Jae Gil Lee, Tae-jin Lee, Jiyong Soon, Ji Heon Ryu, Jin Seok Lee, Seung M. Oh*
Journal : Journal of Power Sources 2017 (370) 131-137
Publication Date : 2017.10.02

This publication is from Prof. Jin
Seok Lee’s collaboration research